What is Outcome Based Education (OBE)?
Outcome-Based Education (OBE) had been implemented in the Kulliyyah of Engineering, in accordance with the directives of the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia and the Board of Engineers Malaysia (BEM).
This is also one of the requirements for Malaysia to become a full member of the Washington Accord (WA), an international agreement to mutually recognize Bachelor degrees in the field of engineering.
OBE is an internationally practiced educational model that focuses on the measurement of student outcomes and the implementation of corrective measures to overcome challenges in the achievements of learning and program outcomes.
Curriculum is designed with specific learning outcomes (LOs) to prepare the graduates to achieve the graduate attributes / programme outcomes (POs) at the point of graduation.
The POs are designed to produce graduates who are well-prepared to achieve the programme educational objectives (PEOs) 3 – 5 years after they have graduated. The PEOs and POs had been formulated in consultation with all major stakeholders (employers, alumni and students), to meet the demands of a challenging and globalized workplace.
Program Educational Objectives (PEO)
A Graduate is expected to achieve one or more of the following program educational objectives.
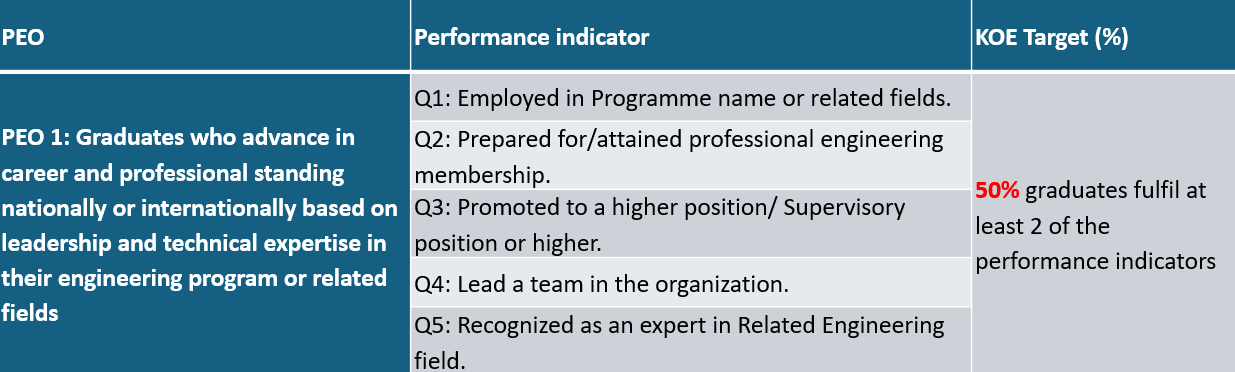
Graduates who advance in career and professional standing nationally or internationally based on leadership and/or technical expertise in the related Engineering Programmes and fields.
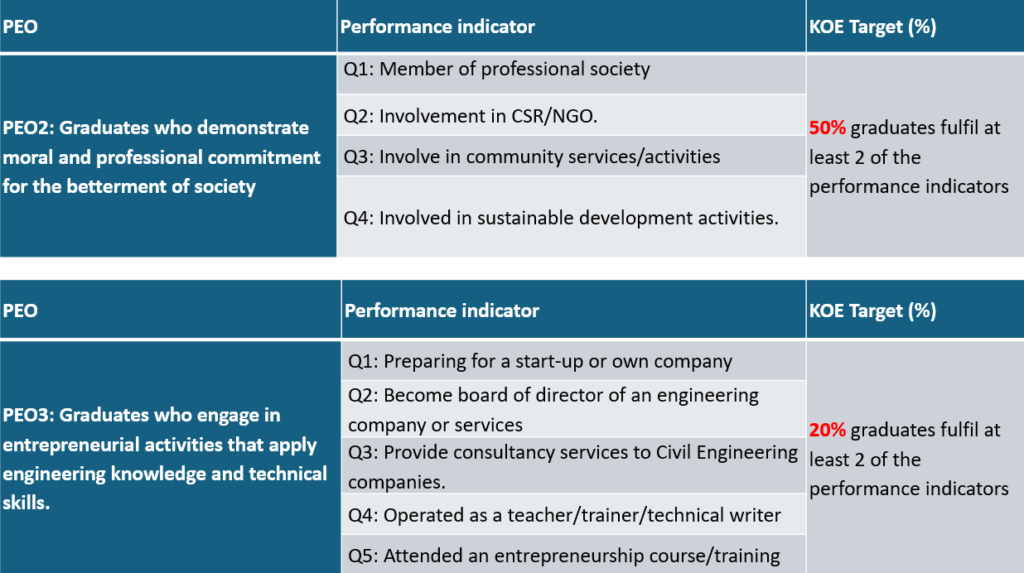
Graduates who demonstrate moral and professional commitment for the betterment of society.
Graduates who engage in entrepreneurial activities that apply engineering knowledge and technical skills.
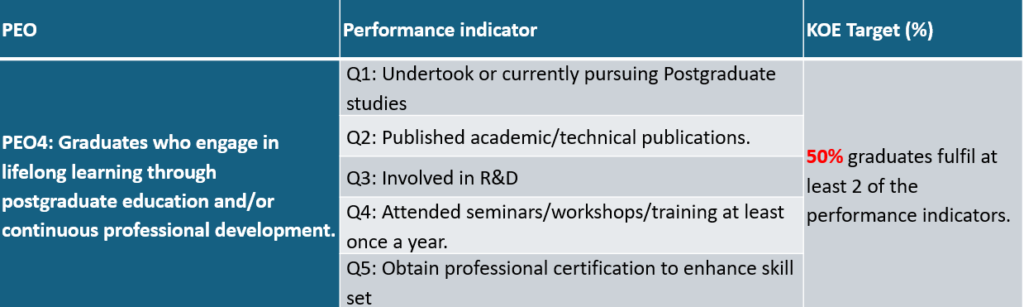
Graduates who engage in lifelong learning through postgraduate education and/or continuous professional development.
PEO Performance Indicator
Program Outcomes (POs) based on EAC Manual 2024
Students graduated from the Kulliyyah of Engineering programmes should have the ability to:
1.Engineering Knowledge – Apply knowledge of mathematics, natural science, computing and engineering fundamentals, and an engineering specialization as specified in WK1 to WK4 respectively to develop solutions to CEPs
2.Problem Analysis – Identify, formulate, research literature and analyze CEPs reaching substantiated conclusions using first principles of mathematics, natural sciences and engineering sciences with holistic considerations for sustainable development (WK1 to WK4)
3.Design/ Development of Solutions – Design creative solutions for CEPs and design systems, components or processes to meet identified needs with appropriate consideration for public health and safety, whole-life cost, net zero carbon as well as resource, cultural, societal, and environmental considerations as required (WK5)
4.Investigation – Conduct investigation of CEPs using research methods including research-based knowledge, including design of experiments, analysis and interpretation of data, and synthesis of information to provide valid conclusions (WK8)
5.Tool Usage – Create, select and apply, and recognize limitation of appropriate techniques, resources, and modern engineering and IT tools, including prediction and modelling, to CEPs, (WK2 and WK6)
6.The Engineer and the World – Analyze and evaluate sustainable development impacts to: society, the economy, sustainability, health and safety, legal frameworks, and the environment, in solving CEPs (WK1, WK5, and WK7)
7.Ethics – Apply ethical principles and commit to professional ethics with Islamic values and norms of engineering practice and adhere to relevant national and international laws. Demonstrate an understanding of the need for diversity and inclusion (WK9)
8.Individual and Collaborative Teamwork – Function effectively as an individual, and as a member or leader in diverse and inclusive teams and in multidisciplinary, face-to-face, remote and distributed settings (WK9)
9.Communication – Communicate effectively and inclusively on complex engineering activities with the engineering community and with society at large, such as being able to comprehend and write effective reports and design documentation, make effective presentations, considering cultural, language, and learning differences
10.Project Management and Finance – Apply knowledge and understanding of engineering management principles and economic decision-making and apply these to one’s own work, as a member and leader in a team, and to manage projects in multidisciplinary environments;
11.Lifelong Learning – Recognize the need for, and have the preparation and ability for independent and life-long learning adaptability to new and emerging technologies and critical thinking in the broadest context of technological change (WK8).
The POs are directly mapped to relevant courses and explicitly mapped to the LOs of the related courses.
Learning Outcomes (COs) are the expected outcomes of each course, and it is what student should be able to do upon the completion of a specific course. Each course has a set of learning outcomes which are explicitly linked to specific POs.
LOs are assessed and evaluated through various measurement/assessment tools. At the end of the measurement, the COs attainment will directly contribute to the achievement of specific POs linked to it.
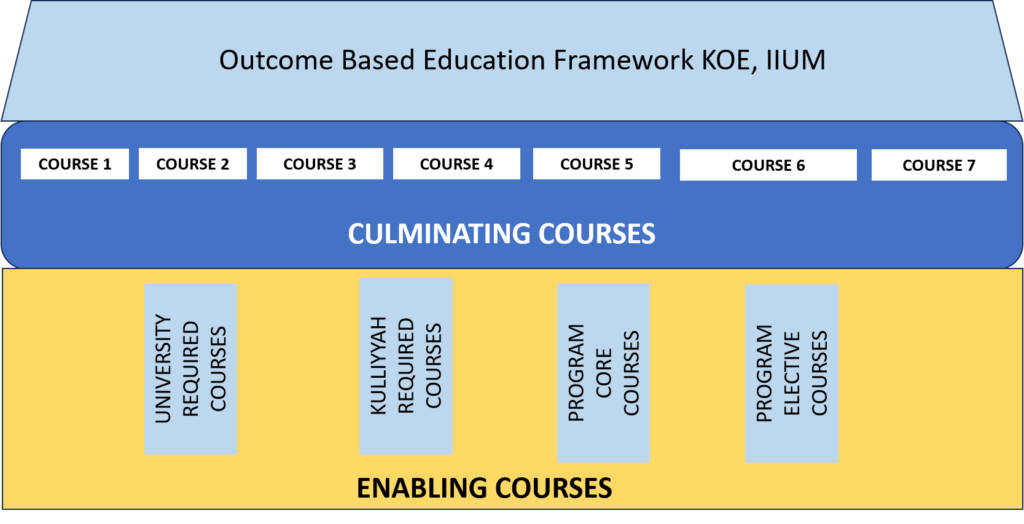
OBE Framework at KOE
OBE framework at KOE-IIUM categorize courses into enabling and culminating courses