December 5th, 2024
by Nurizzuwa Natasya Mohamed Muzni
Location: Kobe City College & University of Hyogo, Kobe, Japan.
The Elective Disaster Nursing Mobility Outbound program to Kobe, Japan, provided a transformative opportunity for eight students from the Kulliyyah of Nursing, IIUM, to enhance their knowledge and skills in disaster nursing. Hosted by Kobe City College of Nursing and the University of Hyogo, the program took place from 26th November to 4th December 2024 and served as a platform for hands-on learning and global collaboration.
Participation in the 8th International Research Conference on Disaster Nursing
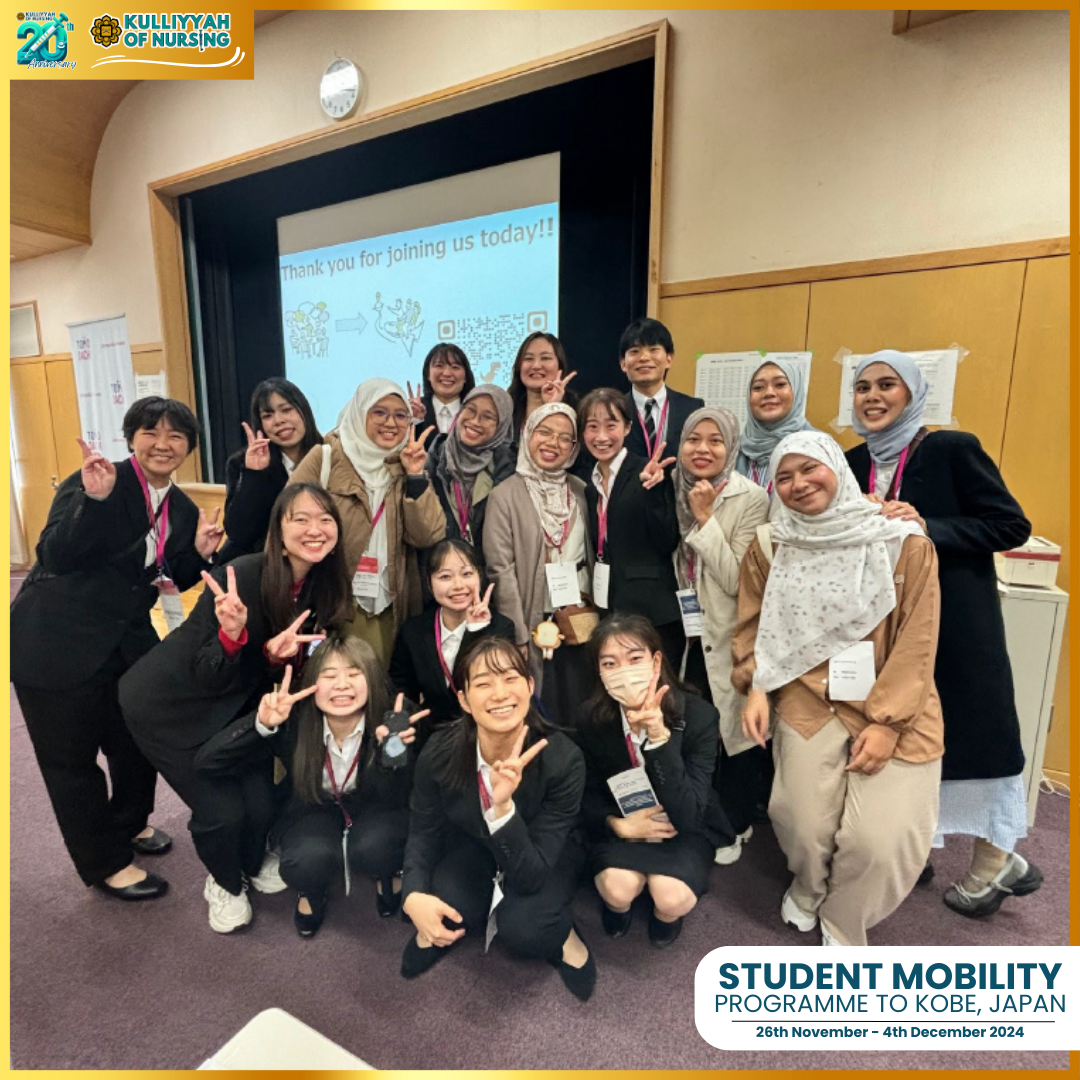
A key highlight of the program was the students’ participation in the 8th International Research Conference of the World Society of Disaster Nursing. The conference brought together leading researchers and practitioners, allowing participants to engage in meaningful discussions and gain insights into the latest advancements in disaster nursing.
Guidance and Support
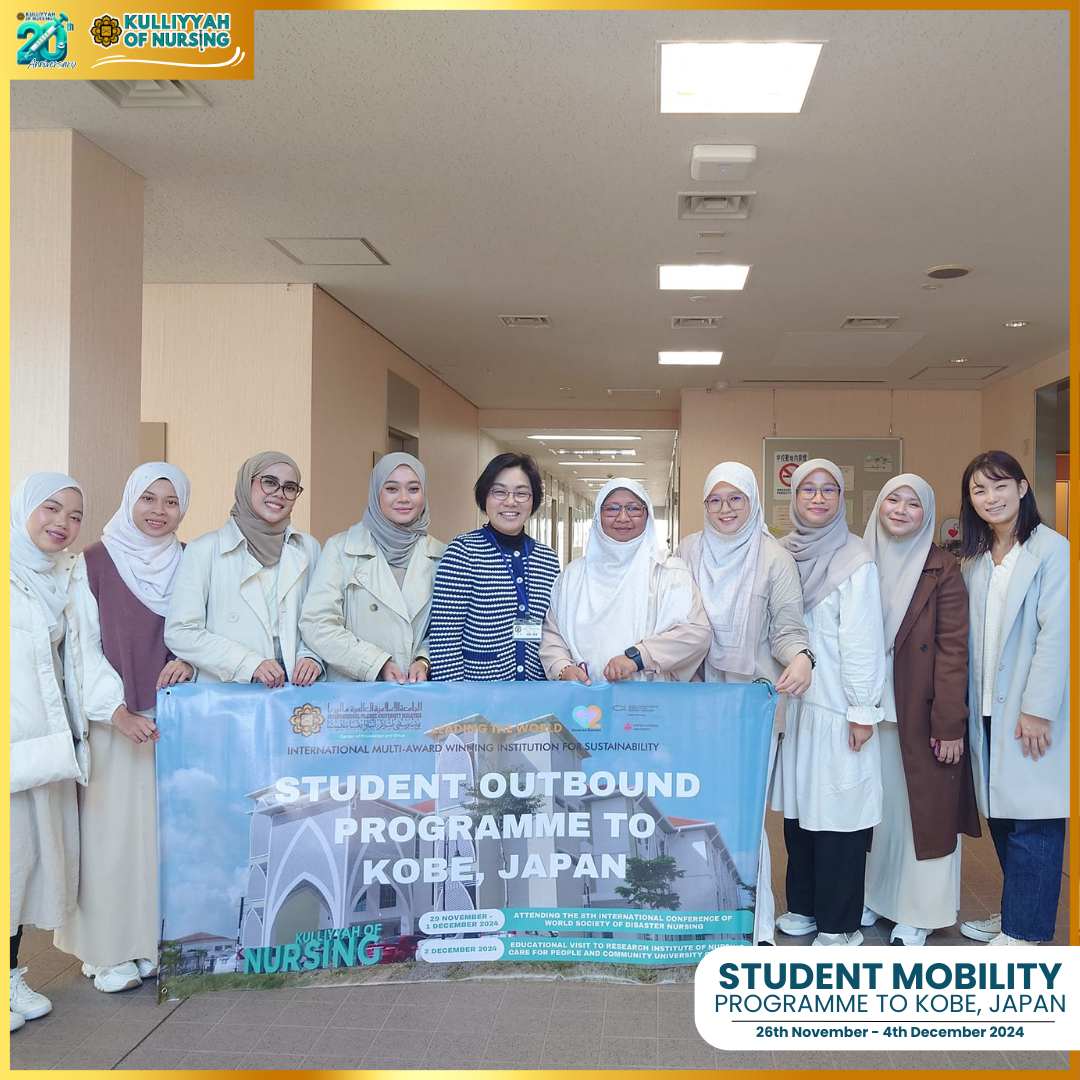
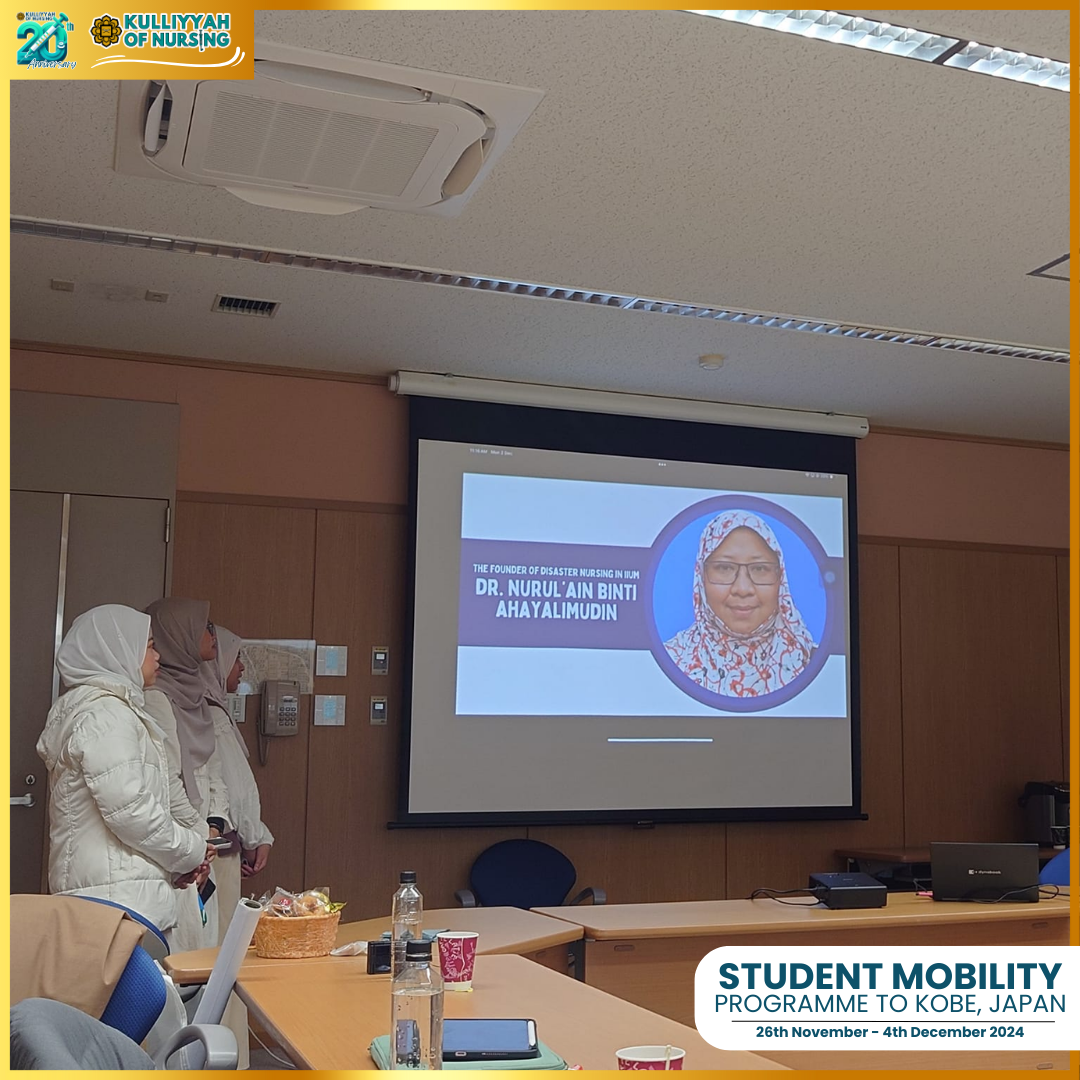
The students were accompanied by Dr. Nurul’Ain Ahayalimudin, who provided guidance and support throughout the program. Her expertise and mentorship added tremendous value to the Kulliyyah of Nursing students’ overall experience.
Cultural Immersion and Advanced Learning
Participants gained deeper insights into international practices, guidelines, and strategies in disaster nursing. Exposure to diverse cultural approaches to disaster management enabled them to understand and adapt these practices to suit local contexts. This cultural exchange also heightened their appreciation for the role of nurses in disaster preparedness and response.
Key Achievements
Through the program, Kulliyyah of Nursing students accomplished several significant outcomes:
- Gained a deeper understanding of international practices, guidelines, and strategies in disaster nursing.
- Learned how different cultures approach disaster management and adapted these methods to local contexts.
- Developed a heightened awareness of the critical roles nurses play during disasters, emphasizing their importance in providing care and support during crises.
Conclusion
The program was highly effective in increasing the students’ knowledge and skills in disaster nursing. Participants learned about worldwide practices, rules, and methods, which helped them identify new approaches to improve disaster preparedness and response in their home countries. They were exposed to various cultural methodologies, allowing them to adapt and apply disaster management strategies effectively in local contexts. Moreover, the program highlighted the critical role that nurses play during disasters, emphasizing their value in providing treatment and assistance in difficult times. It also provided students with opportunities to connect with others, discuss ideas, and encourage collaboration in preparation for future disaster nursing teams. This experience not only equipped Kulliyyah of Nursing students for the future but also strengthened disaster response efforts locally and internationally.
Gallery